DyW Physiological Data
In the DyW strain (B6.129S1(Cg)-Lama2tm1Eeng/J, 013786), knock-out of the laminin alpha 2 gene models merosin-deficient congenital muscular dystrophy. Homozygous dyW mice are passive, small, and emaciated, and demonstrate partial hindleg lameness and clasping. Their muscles contain necrotic fibers with occasional areas of regeneration, and they exhibit pronounced fibrosis and increased creatine kinase (CK) activity.
Return to Muscular Dystrophy Efficacy Studies
Ambulation & Strength
Righting Reflex in DyW
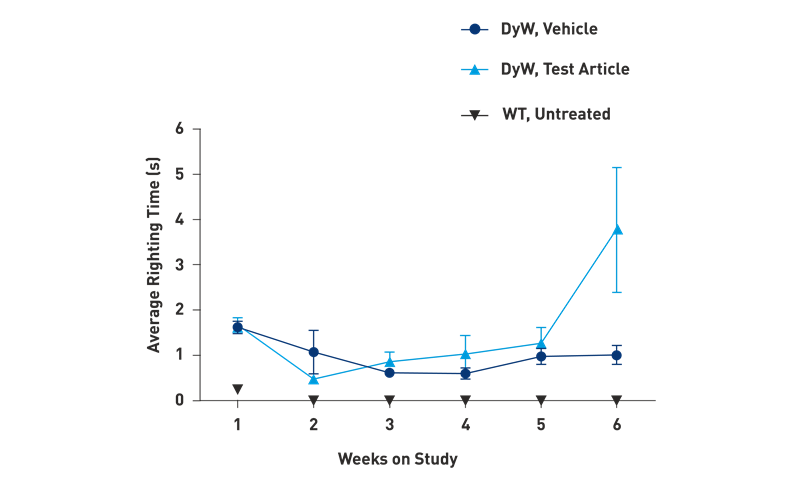
For mouse models with early-onset muscle disease and severe loss of ambulation, the open field test is not appropriate. Instead, the time for mice to right themselves after being placed on their back is measured. Wild type (WT) mice immediately right themselves, while DyW mutants present a robust, delayed righting reflex. In this example, a test article administered for 6 weeks only mildly, and transiently improved the righting reflex.
Grip Strength
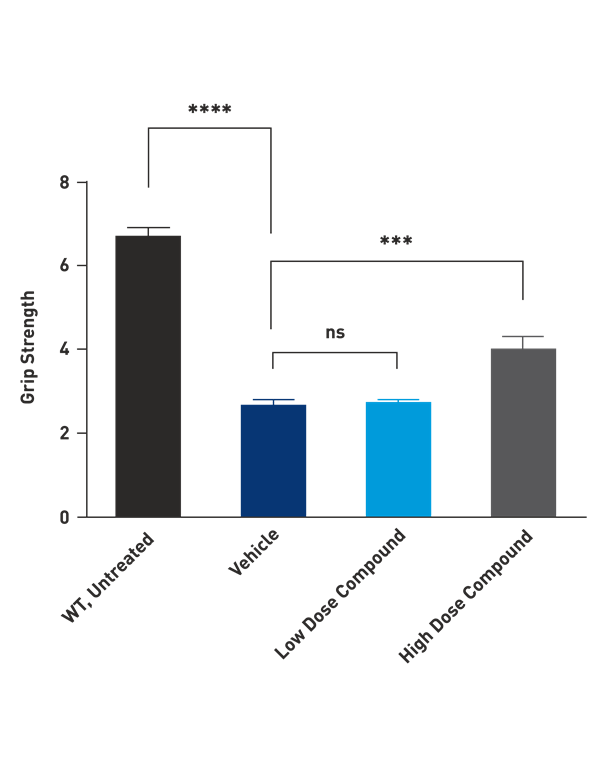
Grip strength is measured by a grip-strength meter. DyW mice (Vehicle) are weaker than the wild type controls. Grip strength is partially restored by treating DyW mice with a High Dose of the test compound.
Muscle Damage
Serum CK in DyW
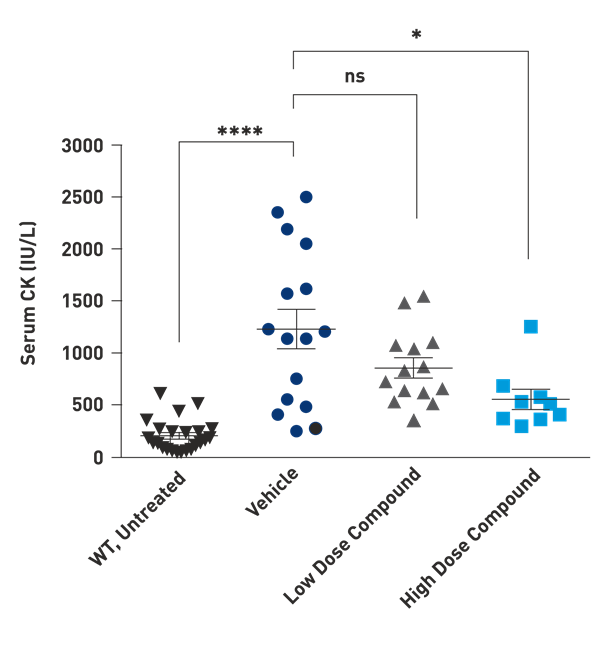
Serum creatine kinase (CK) is an indicator of muscle injury. DyW mice show an increase in serum CK level (Vehicle) compared to wild type mice (WT, untreated). When treated with a test compound, dyW mice had a dose dependent decrease in serum CK levels.